Choosing the right size air conditioner is crucial for maintaining a comfortable indoor environment and ensuring energy efficiency. This guide will help you understand the factors to consider when selecting an air conditioner size for your space.
Air Conditioner Size Guide
An often overlooked factor contributing to air conditioner inefficiency is improper sizing. An AC unit that’s too small for your space will constantly struggle to keep up, leading to higher energy bills and reduced comfort. Conversely, an oversized unit will cycle on and off too frequently, reducing efficiency and potentially creating humidity issues. To avoid these problems, consult an HVAC professional to determine the correct size unit for your home. They will consider factors like square footage, insulation levels, and sun exposure. By ensuring your AC is properly sized, you’ll be setting yourself up for optimal performance and fewer headaches down the road. For more information on “AIR CONDITIONING PROBLEMS AND THEIR SIMPLE SOLUTION“, you can find many resources online and from qualified technicians.
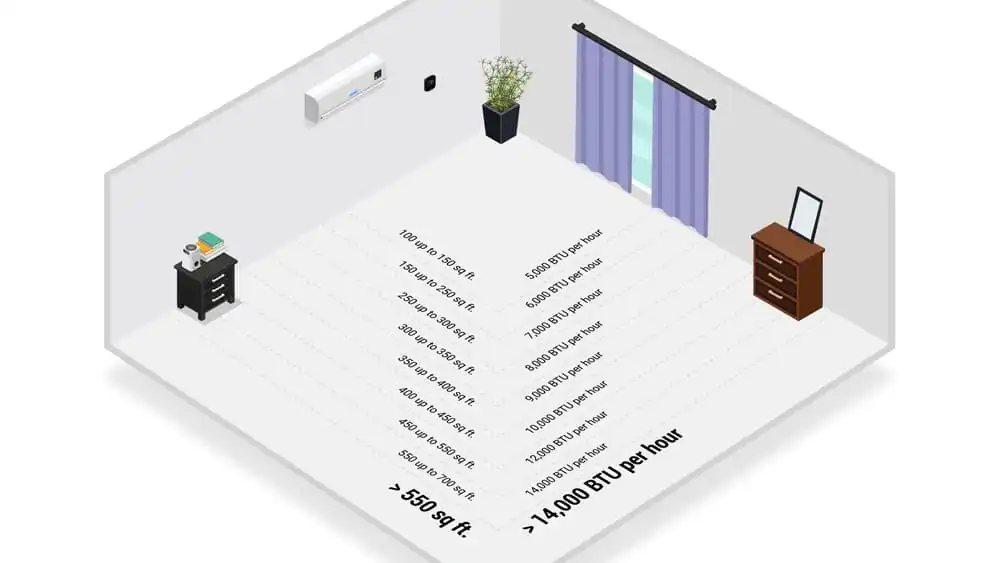
Understanding BTUs
The capacity of an air conditioner is measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs). BTUs indicate the amount of heat an air conditioner can remove from a room per hour. Choosing an air conditioner with the appropriate BTU rating is essential to ensure it cools the space effectively without wasting energy.
Calculating BTUs for Your Room
To determine the right BTU rating for your room, you need to consider the room’s square footage. Here’s a general guideline:
- Up to 150 sq. ft.: 5,000 BTUs
- 150 – 250 sq. ft.: 6,000 BTUs
- 250 – 300 sq. ft.: 7,000 BTUs
- 300 – 350 sq. ft.: 8,000 BTUs
- 350 – 400 sq. ft.: 9,000 BTUs
- 400 – 450 sq. ft.: 10,000 BTUs
- 450 – 550 sq. ft.: 12,000 BTUs
- 550 – 700 sq. ft.: 14,000 BTUs
- 700 – 1,000 sq. ft.: 18,000 BTUs
- 1,000 – 1,200 sq. ft.: 21,000 BTUs
Factors Affecting Air Conditioner Size
Several factors can influence the required BTU rating beyond just room size. Consider the following aspects when selecting an air conditioner.
Room Characteristics
- Ceiling Height: Higher ceilings increase the volume of air that needs cooling. For rooms with ceilings higher than 8 feet, you may need an air conditioner with a higher BTU rating.
- Insulation: Well-insulated rooms retain cool air more effectively, potentially reducing the required BTU rating. Conversely, poorly insulated spaces may need a more powerful air conditioner.
- Sun Exposure: Rooms with significant sun exposure, especially during the hottest parts of the day, will require more cooling power. Consider increasing the BTU rating by 10-20% for these areas.
Occupancy and Appliances
- Number of Occupants: Each person generates body heat, contributing to the overall temperature. For rooms frequently occupied by multiple people, add an additional 600 BTUs per person.
- Heat-Generating Appliances: Kitchens and rooms with numerous electronic devices may need additional cooling capacity. Account for these heat sources when determining the appropriate BTU rating.
Choosing the Right Air Conditioner

Types of Air Conditioners
There are various types of air conditioners available, each suitable for different applications and room sizes. Here are the main types to consider:
Window Air Conditioners
Window air conditioners are a popular choice for single rooms. They are installed in a window or a custom opening in a wall. These units are relatively easy to install and can be removed when not in use.
Portable Air Conditioners
Portable air conditioners are standalone units that can be moved from room to room. They typically require a window for venting hot air. These units offer flexibility but may not be as efficient as other types.
Split Air Conditioners
Split air conditioners consist of an indoor and an outdoor unit. They are more efficient and quieter than window or portable units. Split air conditioners are suitable for cooling larger areas or multiple rooms.
Central Air Conditioning
Central air conditioning systems are designed to cool entire homes. They distribute cool air through a network of ducts. While they require a significant upfront investment, they offer superior cooling performance and energy efficiency.
Installation and Maintenance Tips

Proper Installation
Correct installation is critical for the optimal performance of your air conditioner. Ensure that the unit is securely mounted and that all seals are airtight. For window units, use brackets if necessary to support the weight and prevent tilting.
Regular Maintenance
- Clean or Replace Filters: Dirty filters reduce efficiency and can lead to system malfunctions. Clean or replace filters every 1-2 months during the cooling season.
- Check for Leaks: Inspect the unit for any signs of refrigerant leaks. Low refrigerant levels can compromise the cooling capacity and increase energy consumption.
- Schedule Professional Servicing: Have your air conditioner serviced by a professional at least once a year. Regular maintenance can extend the lifespan of your unit and ensure it operates efficiently.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Selecting an energy-efficient air conditioner can significantly reduce your energy bills. Look for units with a high Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) or Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER). Additionally, consider models with Energy Star certification, which meet stringent efficiency standards set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Conclusion
Choosing the right size air conditioner involves understanding BTU ratings, considering room characteristics, and selecting the appropriate type of unit. By taking these factors into account, you can ensure a comfortable and energy-efficient cooling solution for your space. Regular maintenance and proper installation will further enhance the performance and longevity of your air conditioner, providing you with a reliable cooling system for years to come.
